みなさん、こんにちは。第5回目となる今回は、コンストラクタとデストラクタについてお話しします。
コンストラクタ
コンストラクタとは、クラスにおいてオブジェクトが生成された際に実行されるメソッドのことです。コンストラクタの良くある使い方としては、例えばオブジェクト生成時のインスタンス変数の初期化が挙げられます。
construct_1.php
<?php
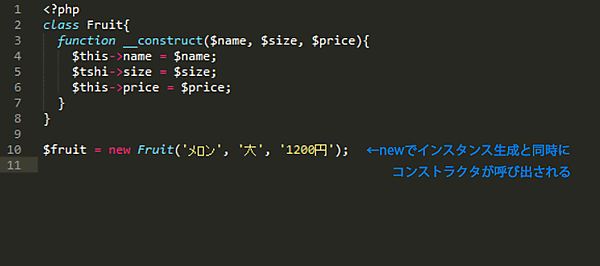
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function __construct($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = $name;
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
このような書き方を良く見かけると思います。上記の例では、Fruitインスタンスを生成する時に、名前とサイズと金額をそれぞれ引数として渡し、コンストラクタでインスタンス変数に渡します。その後、それぞれのゲッターメソッドで名前やサイズ、金額を取得できるようにする、というようなクラスの書き方は、一般的に行われています。
construct_2.php
<?php
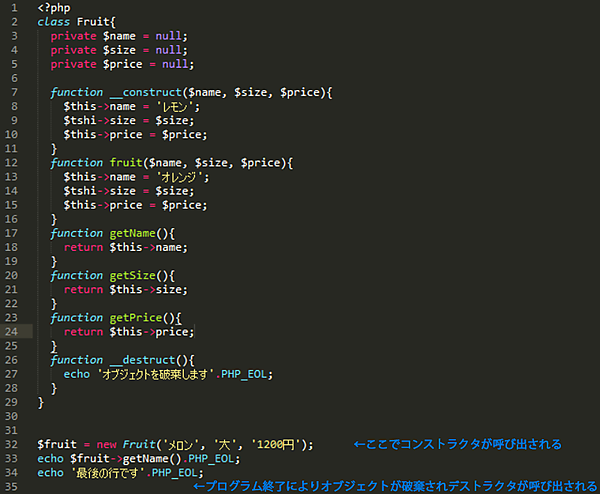
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function __construct($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = $name;
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
function getName(){
return $this->name;
}
function getSize(){
return $this->size;
}
function getPrice(){
return $this->price;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
echo $fruit->getName();
出力結果
$ php construct_2.php
メロン
上記の例では、「__construct」という名前でコンストラクタを定義しています。クラス名と同じ名前のメソッド(この例では「Fruit」)を定義することで、コンストラクタとすることも可能ですが、これは古い指定方法です。
construct_3.php
<?php
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function Fruit($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = $name;
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
function getName(){
return $this->name;
}
function getSize(){
return $this->size;
}
function getPrice(){
return $this->price;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
echo $fruit->getName();
出力結果
$ php construct_3.php
メロン
デストラクタ
デストラクタはコンストラクタの逆に、オブジェクトが参照されなくなった時に確実に実行されるメソッドです。
destruct_1.php
<?php
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function __construct($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = 'レモン';
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
function getName(){
return $this->name;
}
function getSize(){
return $this->size;
}
function getPrice(){
return $this->price;
}
function __destruct(){
echo 'オブジェクトを破棄します'.PHP_EOL;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
echo $fruit->getName().PHP_EOL;
echo '最後の行です'.PHP_EOL;
出力結果
$ php destruct_1.php
レモン
最後の行です
オブジェクトを破棄します
スクリプト終了と同時にオブジェクトが破棄されるため、デストラクタが呼び出され「オブジェクトを破棄します」と出力されていることがわかります。
次の例のように、unsetやnullを代入するとオブジェクトが破棄されるので、デストラクタはそのタイミングで呼び出されます。
destruct_2.php
<?php
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function __construct($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = $name;
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
function getName(){
return $this->name;
}
function getSize(){
return $this->size;
}
function getPrice(){
return $this->price;
}
function __destruct(){
echo 'オブジェクトを破棄します'.PHP_EOL;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
echo $fruit->getName().PHP_EOL;
$fruit = null;
echo '最後の行です'.PHP_EOL;
出力結果
$ php destruct_2.php
メロン
オブジェクトを破棄します
最後の行です
destruct_3.php
<?php
class Fruit{
private $name = null;
private $size = null;
private $price = null;
function __construct($name, $size, $price){
$this->name = $name;
$this->size = $size;
$this->price = $price;
}
function getName(){
return $this->name;
}
function getSize(){
return $this->size;
}
function getPrice(){
return $this->price;
}
function __destruct(){
echo 'オブジェクトを破棄します'.PHP_EOL;
}
}
$fruit = new Fruit('メロン', '大', '1200円');
echo $fruit->getName().PHP_EOL;
unset($fruit);
echo '最後の行です'.PHP_EOL;
出力結果
$ php destruct_3.php
メロン
オブジェクトを破棄します
最後の行です
デストラクタは、「オブジェクトが破棄される際にログに書き出す」などに加えて、スクリプト終了時に確実に実行されることを利用して、開いたままになっているファイルを閉じるなどの使い道があります。
次の例で見てみましょう。
destruct_file.php
<?php
class File{
private $handle = null;
function __construct($path){
$this->handle = fopen($path, 'r+');
flock($this->handle, LOCK_EX);
}
function write($text){
fwrite($this->handle, $text);
return true;
}
function read(){
$result = null;
while ($line = fgets($this->handle)) {
$result .= $line.PHP_EOL;
}
return $result;
}
function __destruct(){
flock($this->handle, LOCK_UN);
fclose($this->handle);
echo 'ファイルを閉じて終了します。'.PHP_EOL;
}
}
$file = new File('./written_file.txt');
echo $file->read().PHP_EOL;
$file->write('試しに書いてみます'.PHP_EOL);
二回続けて実行してみます。
出力結果
$ php destruct_file.php
元から書いてある文章
ファイルを閉じて終了します。
$ php destruct_file.php
元から書いてある文章
試しに書いてみます
ファイルを閉じて終了します。
このように、デストラクタでファイルロックを解除してクローズしておけば、オブジェクトが破棄される時にファイルがクローズされるため、「閉じ忘れて他の処理をしている間ずっとロックされたまま」といったことを防げます。