はじめに
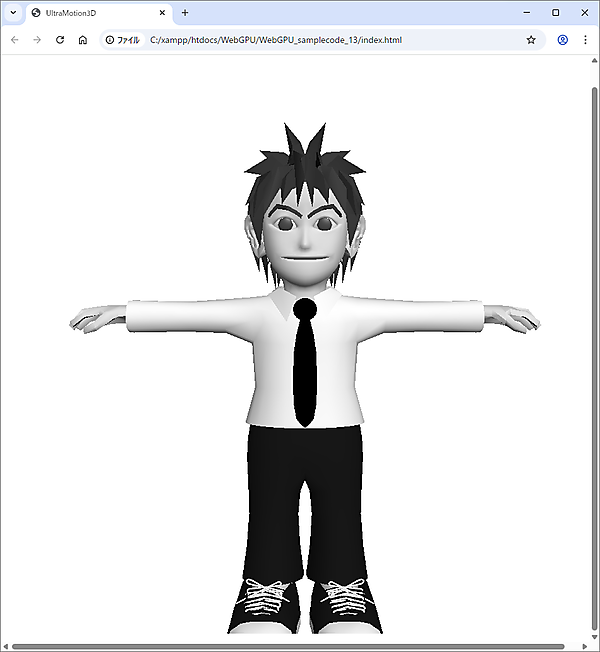
今回は、キャラクターモデルとしてダウンロードした「webgpu.zip」に入っている「models/Character.js」データを使います。まずは「ボーン(骨)」をセットしますが、今回は図1のように初期位置のままでアニメーションはせず、T字ポーズをとるだけです。
アニメーションなしのボーンを実装する
今回は、新たに「BoneModel3D」クラスが登場します。「Model3D」クラスにボーン機能を肉付けしたものです。便宜上、できるだけ省略せずにサンプルコードを書いたため、今までと比べてもかなり長くなりましたが、追加するコードはそれほど多くないと思います。BoneModel3DクラスはModel3Dクラスをコピペしたところも多いです。
パイプラインを実装する
前回までのようにメインコードとシェーダーとを綱渡しするパイプラインで、ボーン番号を表す4byte*1個も追加します。またユニフォームバッファに16(4×4行列の要素数)*32ボーンのオフセットも足します。32ボーンという数は体・左右手足・頭など骨の数を適当に最大32個と決めました。
・サンプルコード「lib」→「UltraMotion3D.js」var _lastTime = 0;
var _elapsed = 0;
var _num = 0;
var _camera = new Matrix3D();
var _fov = 45.0;
const MAX_NUM = 10000;
const BONE_MAX = 32;
const UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE = 4 * 16 * (4 + BONE_MAX); // 4byte(float32) * 4x4 matrix * (4 + 32)
const OFFSET_SIZE = UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE; //256の倍数
var _passEncoder = null;
async function initWebGPU(canvas) {
if (!navigator.gpu) {
throw Error('WebGPU not supported.');
}
const adapter = await navigator.gpu.requestAdapter();
if (!adapter) {
throw Error('Could not request WebGPU adapter.');
}
_device = await adapter.requestDevice();
_canvas = document.getElementById(canvas);
_context = _canvas.getContext('webgpu');
_presentationFormat = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat();
_context.configure({
device: _device,
format: _presentationFormat,
alphaMode: 'premultiplied',
});
_pipeline = setPipeline(vertWGSL,fragWGSL);
_pipelineTexture = setPipeline(vertWGSL,fragTextureWGSL);
_pipelineBone = setPipeline(vertBoneWGSL,fragWGSL);
_pipelineBoneTexture = setPipeline(vertBoneWGSL,fragTextureWGSL);
_uniformBuffer = _device.createBuffer({
size: UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE + OFFSET_SIZE * MAX_NUM,
usage: GPUBufferUsage.UNIFORM | GPUBufferUsage.COPY_DST,
});
window.addEventListener("resize", resize, false);
resize();
init();
requestAnimationFrame(everyFrame.bind(everyFrame));
}
function setPipeline(vertexWGSL,fragmentWGSL) {
const pipeline = _device.createRenderPipeline({
layout: 'auto',
vertex: {
module: _device.createShaderModule({
code: vertexWGSL,
}),
entryPoint: 'main',
buffers: [{
attributes: [
{// position
shaderLocation: 0,
offset: 0,
format: 'float32x4',
},{// normal
shaderLocation: 1,
offset: 4*4,
format: 'float32x3',
},{// color
shaderLocation: 2,
offset: 4*(4+3),
format: 'float32x4',
},{// specular
shaderLocation: 3,
offset: 4*(4+3+4),
format: 'float32',
},{// uv
shaderLocation: 4,
offset: 4*(4+3+4+1),
format: 'float32x2',
},{// bone
shaderLocation: 5,
offset: 4*(4+3+4+1+2),
format: 'float32',
},
],
arrayStride: 4*(4+3+4+1+2+1),
stepMode: "vertex",
},],
},
fragment: {
module: _device.createShaderModule({
code: fragmentWGSL,
}),
entryPoint: 'main',
targets: [// 0
{
format: _presentationFormat,
},
],
},
primitive: {
topology: 'triangle-list',
},
depthStencil: {
depthWriteEnabled: true,
depthCompare: 'less',
format: 'depth24plus',
},
});
return pipeline;
}
(後略)【サンプルコードの解説】
「_lastTime」変数は1フレーム前の時間、「_elapsed」変数は経過時間です。60FPSでだいたい1/60の値になります。
「BONE_MAX」定数は32個のボーン数です。
「UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE」は1つのモデル(Model3Dクラス)、または1つのボーンモデル(BoneModel3Dクラス)ごとに必要となるユニフォームバッファのサイズです。
パイプラインでは「shaderLocation」の5番目にオフセットを4*(4+3+4+1+2)に設定し、ボーン番号を渡します。
「arrayStride」で1頂点ごとに「4*(4+3+4+1+2+1)」の要素数だけ頂点データを渡します。
BoneModel3Dクラスを実装する
新たに「lib/BoneModel3D.js」ファイルを作成します。BoneModel3DクラスはModel3Dクラスを継承したクラスで、Model3Dクラスのモデルデータにボーンとアニメーションデータを追加します。
キャラクターデータの「Character」クラスはBoneModel3Dクラスを継承したクラスで、新たに「setB」メソッド、「setBI」メソッド、「setMatrix」メソッド、「setMatri2」メソッド、「setMatrix3」メソッドが出てきます。
・サンプルコード「lib」→「BoneModel3D.js」class BoneModel3D extends Model3D {
constructor() {
super();
}
setB(x,y,z,nx,ny,nz,material,u,v,bone,parent,weight) {
this.preVertices.push(x,y,z,nx,ny,nz,material,u,v,bone);
}
setBI(i0,i1,i2) {
var indices = [];
indices.push(i0,i1,i2);
for ( let i = 0; i < indices.length; i++ ) {
const j = indices[i];
const x = this.preVertices[j*10 ];
const y = this.preVertices[j*10+1];
const z = this.preVertices[j*10+2];
const nx = this.preVertices[j*10+3];
const ny = this.preVertices[j*10+4];
const nz = this.preVertices[j*10+5];
const m = this.preVertices[j*10+6];
const r = this.materials[m].r;
const g = this.materials[m].g;
const b = this.materials[m].b;
const a = this.materials[m].a;
const s = this.materials[m].spc;
const u = this.preVertices[j*10+7];
const v = this.preVertices[j*10+8];
const bn = this.preVertices[j*10+9];
this.vertices.push(x,y,z,1,nx,ny,nz,r,g,b,a,s,u,v,bn);
}
}
setMatrix(matrix) {
}
setMatrix2() {
}
setMatrix3(materials) {
}
initBuffers() {
this.vertexArray = new Float32Array(this.vertices);
this.verticesBuffer = _device.createBuffer({
size: this.vertexArray.byteLength,
usage: GPUBufferUsage.VERTEX,
mappedAtCreation: true,
});
new Float32Array(this.verticesBuffer.getMappedRange()).set(this.vertexArray);
this.verticesBuffer.unmap();
if ( this.materials[0].texture ) this.initTexture();
else this.init();
}
async init() {
this.uniformBindGroup = _device.createBindGroup({
layout: _pipelineBone.getBindGroupLayout(0),
entries: [
{
binding: 0,
resource: {
buffer: _uniformBuffer,
offset: OFFSET_SIZE*this.num,
size: UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE,
},
},
],
});
}
async initTexture() {
let imageTexture = await loadTexture(this.materials[0].texture);
const sampler = _device.createSampler({
magFilter: 'linear',
minFilter: 'linear',
});
this.uniformBindGroup = _device.createBindGroup({
layout: _pipelineBoneTexture.getBindGroupLayout(0),
entries: [
{
binding: 0,
resource: {
buffer: _uniformBuffer,
offset: OFFSET_SIZE*this.num,
size: UNIFORM_BUFFER_SIZE,
},
},{
binding: 1,
resource: sampler,
},{
binding: 2,
resource: imageTexture.createView(),
},
],
});
}
draw() {
if (this.uniformBindGroup) {
if ( this.materials[0].texture ) _passEncoder.setPipeline(_pipelineBoneTexture);
else _passEncoder.setPipeline(_pipelineBone);
this.setTransform();
this.setAnimation();
_passEncoder.setBindGroup(0,this.uniformBindGroup);
_passEncoder.setVertexBuffer(0,this.verticesBuffer);
_passEncoder.draw(this.getVertexCount());
}
}
setAnimation() {
let matrices = new Float32Array(BONE_MAX*16);
let matrix = new Matrix3D();
for (let i = 0; i < 16*BONE_MAX; i++ ) matrices[i] = matrix.e[i%16];
_device.queue.writeBuffer(
_uniformBuffer,
4 * 16 * 4 + OFFSET_SIZE*this.num,
matrices.buffer,
0,
4 * 16 * BONE_MAX
);
}
}【サンプルコードの解説】
setBメソッドでボーン付き頂点データを1頂点ずつ追加します。
setBIメソッドではボーン付き頂点を三角形の3頂点分のインデックスで指定し、それらを「vertices」配列に追加します。
「init()」メソッドでは「createBindGroup」の「layout」に「_pipelineBone」パイプラインを使用します。一方、「initTexture()」メソッドではcreateBindGroupのlayoutに「_pipelineBoneTexture」パイプラインを使用します。
「setMatrix」メソッド、「setMatrix2」メソッド、「setMatrix3」メソッドは暫定的に用意しているだけで何もしません。
「setAnimation」関数では、この回だけ暫定的に「1次元」の「matrices」配列にBONE_MAX(32個)×行列の要素数(16個)のボーン行列を入れます。モデル・ビュー・プロジェクション・法線行列の後ろ(オフセットが4 * 16 * 4 + OFFSET_SIZE*this.num)にボーン行列の配列をセットします。今回のボーン行列は全て単位行列(Matrix3Dクラスのコンストラクタの初期値)です。
Model3Dクラスを実装する
シェーダーのパイプライン設定を使い回せるように、静止モデルのModel3Dクラスでも頂点データにボーン番号0(意味は特にありません)を追加します。これにより、1頂点あたりの要素数が15個(x,y,z,1,nx,ny,nz,r,g,b,a,s,u,v,bn)になるため、「getVertexCount」メソッドでは 「vertexArray」の要素数を15で除算して頂点数を求めます。
・サンプルコード「lib」→「Model3D.js」class Model3D {
(中略)
setI(i0,i1,i2) {
var indices = [];
indices.push(i0,i1,i2);
for ( let i = 0; i < indices.length; i++ ) {
const j = indices[i];
const x = this.preVertices[j*9 ];
const y = this.preVertices[j*9+1];
const z = this.preVertices[j*9+2];
const nx = this.preVertices[j*9+3];
const ny = this.preVertices[j*9+4];
const nz = this.preVertices[j*9+5];
const m = this.preVertices[j*9+6];
const r = this.materials[m].r;
const g = this.materials[m].g;
const b = this.materials[m].b;
const a = this.materials[m].a;
const s = this.materials[m].spc;
const u = this.preVertices[j*9+7];
const v = this.preVertices[j*9+8];
const bn = 0;
this.vertices.push(x,y,z,1,nx,ny,nz,r,g,b,a,s,u,v,bn);
}
}
initBuffers() {
(中略)
}
async init() {
(中略)
}
async initTexture() {
(中略)
}
getVertexCount() {
return ~~(this.vertexArray.length/15);
}
(中略)
}シェーダーを実装する
Model3Dクラス用の「vertWGSL」定数では、パイプライン定義を揃えるために頂点シェーダーのmain関数へボーン番号の引数だけを形式的に追加します。一方、BoneModel3Dクラス用の「vertBoneWGSL」定数はvertWGSL定数とほぼ同じ構成ですが、ボーン変形のための行列計算を行う点が異なります。「fragWGSL」定数と「fragTextureWGSL」定数は前回までと同じ内容です。
・サンプルコード「lib」→「WGSL.js」const vertWGSL = `
struct Uniforms {
projectionMatrix : mat4x4f,
viewMatrix : mat4x4f,
worldMatrix : mat4x4f,
normalMatrix : mat4x4f,
}
@group(0) @binding(0) var uniforms : Uniforms;
struct VertexOutput {
@builtin(position) position : vec4f,
@location(0) normal : vec3f,
@location(1) color : vec4f,
@location(2) specular : f32,
@location(3) uv : vec2f
}
@vertex
fn main(
@location(0) position: vec4f,
@location(1) normal: vec3f,
@location(2) color: vec4f,
@location(3) specular: f32,
@location(4) uv : vec2f,
@location(5) bone : f32
) -> VertexOutput {
var output : VertexOutput;
output.position = uniforms.projectionMatrix *
uniforms.viewMatrix * uniforms.worldMatrix * position;
output.normal = (uniforms.normalMatrix * vec4f(normal,1)).xyz;
output.color = color;
output.specular = specular;
output.uv = uv;
return output;
}
`;
const vertBoneWGSL = `
struct Uniforms {
projectionMatrix : mat4x4f,
viewMatrix : mat4x4f,
worldMatrix : mat4x4f,
normalMatrix : mat4x4f,
boneMatrix : array,
}
@group(0) @binding(0) var uniforms : Uniforms;
struct VertexOutput {
@builtin(position) position : vec4f,
@location(0) normal : vec3f,
@location(1) color : vec4f,
@location(2) specular : f32,
@location(3) uv : vec2f
}
@vertex
fn main(
@location(0) position: vec4f,
@location(1) normal: vec3f,
@location(2) color: vec4f,
@location(3) specular: f32,
@location(4) uv : vec2f,
@location(5) bone : f32
) -> VertexOutput {
var output : VertexOutput;
var matrix = uniforms.boneMatrix[u32(bone)];
output.position = uniforms.projectionMatrix *
uniforms.viewMatrix * uniforms.worldMatrix * matrix * position;
var n = uniforms.normalMatrix;
var n3x3 = mat3x3f(n[0].xyz,n[1].xyz,n[2].xyz);
var m3x3 = mat3x3f(matrix[0].xyz,matrix[1].xyz,matrix[2].xyz);
output.normal = n3x3 * m3x3 * normal;
output.color = color;
output.specular = specular;
output.uv = uv;
return output;
}
`;
const fragWGSL = `
(中略)
`;
const fragTextureWGSL = `
(中略)
`; 【サンプルコードの解説】
現在のボーン(「bone」引数を整数化したもの)の行列をユニフォームバッファで取得し、モデル・ビュー・プロジェクション行列とともに頂点(position)に乗算して変形します。
法線行列にボーン変形行列も乗算したものを法線(normal)に乗算します。
実行ファイルindex.htmlファイル
それでは、次のサンプルコードをコーディングして「Google Chrome」で「index.html」を実行します。scriptタグで「BoneModel3D.js」ファイルと「Character.js」ファイルを読み込みます。「_model」変数には「Character」クラスのインスタンスを代入します。
・サンプルコード「index.html」<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>UltraMotion3D</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<script src="lib/Material.js"></script>
<script src="lib/Vector3D.js"></script>
<script src="lib/Matrix3D.js"></script>
<script src="lib/Model3D.js"></script>
<script src="lib/BoneModel3D.js"></script>
<script src="lib/WGSL.js"></script>
<script src="lib/UltraMotion3D.js"></script>
<script src="models/Character.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var _model;
function init() {
_model = new Character();
}
function draw() {
_camera.lookAt(new Vector3D(0,200,500),new Vector3D(0,200,0),new Vector3D(0,1,0))
_model.draw();
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload='initWebGPU("CanvasAnimation");'>
<canvas id="CanvasAnimation" width="1800" height="900"></canvas>
</body>
</html>「今やるべきことは何か」を考えてみました。そうしたら「それを見つけるために考えること」が今やるべきことだと閃きました。
おわりに
今回は、前回と変わり映えしない実行結果ですが、ボーン(骨)を埋め込みました。まだユニフォームバッファに渡すボーン行列がどれも単位行列だったので、ポーズには何の変化もありませんでした。
次回は、ついにこの連載も最終回となります。今回はボーンを配置しただけでT字ポーズを取っただけですが、次回はフレームが進むごとにポーズを切り替えていき、アニメーションしているように見せてみます。